
Some common examples of ethers are ethoxyethane (C 2H 5OC 2H 5), methoxy ethane (CH 3OC 2H 5), phenoxy benzene (C 6H 5OC 6H 5), etc.ĭue to the presence of polar atoms of halogens, halides are polar molecules. Ethers do form hydrogen bonds with water and are thus slightly soluble in water. Ether molecules cannot form hydrogen bonds with itself thus, their boiling points are comparable to alkanes of similar mass. The general formula for ethers can be R-O-R, R-O-Ar or Ar-O-Ar where R represents an alkyl group and the Ar represents an aryl group. Some common examples of alcohols are methanol (CH 3OH), ethanol (CH 3CH 2OH), phenol (C 6H 5OH), etc Alcohols can release H+ ions from their hydroxyl groups due to the polarity of the O-H bond. Due to this, alcohols have comparatively higher boiling points. As the hydrogen atoms are attached to oxygen, there is the presence of intermolecular hydrogen bonding. Aldehydes also have less bulky groups around the carbonyl carbon and thus provide a less steric hindrance.Īlcohols are polar due to the presence of oxygen atoms. Some common examples of ketones are propan-2-one (CH 3COCH 3), 1-phenylethanone (C 6H 5COCH 3), benzophenone (C 6H 5COC 6H 5), etc.Īldehydes are more reactive than the ketones, due to a greater partial positive charge on the carbonyl carbon, thus making it a better site for nucleophilic attack. The carbonyl part is reactive and thus the molecule may undergo nucleophilic addition reactions, oxidation, reduction, halogenation reactions, etc. They are slightly soluble in water as they can form hydrogen bonds with water. However, ketones are polar due to the presence of oxygen. Some examples of aldehydes include formaldehyde (HCHO), acetaldehyde (CH 3CHO), benzaldehyde (C 6H 5CHO), etc.Īlso contains carbonyl group but no hydrogen is attached to oxygen, so it does not form hydrogen bonds with itself, so their boiling points are lesser than carboxylic acids of similar mass. Due to the double bond, these compounds are highly reactive and undergo a lot of reactions(nucleophilic addition reactions). They participate in hydrogen bonding in water and thus lower aldehydes are slightly soluble in water. However, there is no hydrogen attached to the oxygen atom thus, they cannot form hydrogen points among themselves. Some examples of esters are ethyl acetate (CH 3COOC 2H 5), propyl methanoate (CH 3COOC 3H 7), etc.ĭue to the presence of the oxygen in the carbonyl group, aldehyde molecules are slightly polar. Ester compounds of lower mass are soluble in water. Thus they have low boiling points compared to carboxylic acids of similar mass.
#Functional groups organic chemistry full
In such types of compounds, the full name of the parent alkane is written before the suffix.Įster molecules are polar due to the presence of electronegative oxygen atoms however, there is no hydrogen attached to the oxygen atoms thus, ester molecules do not participate in hydrogen bonding. If multiple functional groups of the same type are present, the number is indicated by adding di, tri, etc. The chain is numbered in such a way that the carbon to which the functional group is attached gets the lowest possible number in the chain. The longest chain is chosen as the basis. The carbon chain to which the leading functional group is attached is chosen as the main chain. Hence, they are named by their prefix like -R(alkyl), -C 6H 5(benzyl), halogens, -NO 2 (nitro compounds), -OR where R is an alkyl group (alkoxy), etc. Some functional groups are always substituents. COOH (carboxylic acid), -SO 3H (sulphonic acids), -COOR where R is an alkyl group (ester), -COCl (acyl halides), -CONH 2 (amides), -CN(nitriles), -CHO (aldehydes), >C=O(ketones), -OH (alcohols), -NH 2(amines), >C=C< (alkene), -CC- (alkyne, triple bonded) The others would be regarded as the substituents. Whichever group comes first in the priority list, it is given greater importance and would be considered the principal functional group. In order to decide the principal functional group and the groups that will be the substituents, a standard priority list is created. The remaining functional groups called subordinate functional groups (also called substituents) are referred to by using their respective prefixes. In case of compounds with multiple functional groups, a principal functional group is chosen and the compound is named on that basis with the name ending with the suffix related to that functional group. Nomenclature of compounds due to functional groups Organic compounds are thus classified into different classes based on the functional group that is attached to it.
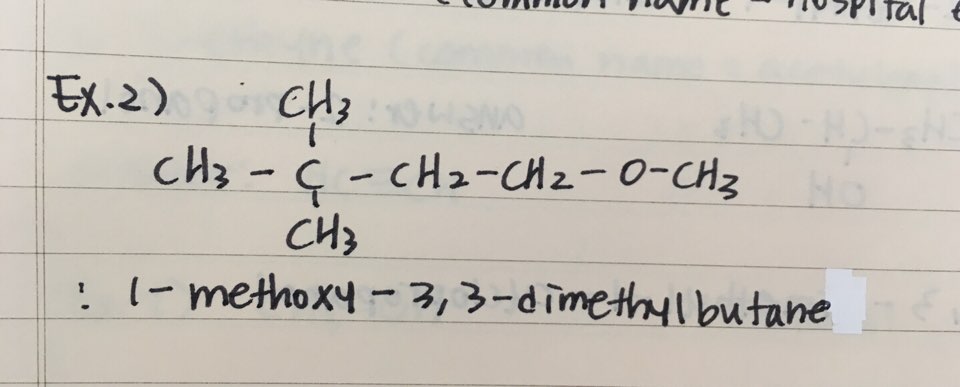
They are also usually the site of chemical activity of the molecule and the site where the reagents attack or interact. They confer special characteristics and properties to the molecule they are attached. Functional groups are an atom or a group of atoms bonded together in a unique manner attached to the alkyl chain or ring or any other organic molecule.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
